“Are you muted?” “Hey, we can’t hear you, I think you’re on mute.”
“Sorry can you repeat that? You froze for a second.”
“Who can volunteer to take notes for this meeting?”
Over two years into the pandemic, a lot of things have changed in the remote work landscape. As more jobs move to remote settings than ever before, the communication between coworkers and customers has shifted to that realm as well. With that shift comes a new set of trials and tribulations that didn’t exist in face-to-face meetings.
Challenges
While there may always be that one coworker who can’t seem to find the mute button, communication platforms, such as Zoom and Teams, have been pushing the limits of effective video conferencing communication for years, even prior to the pandemic. Addressing issues such as video and audio quality, captioning, and transcription with the use of artificial intelligence and machine learning, platforms like Zoom have not just made a more efficient online meeting environment but made it more accessible as well.
Painpoints
Automated transcription and note taking does not just alleviate the burden of the employee who is always designated to take notes “because they are the fastest at typing” but also makes the meeting space more welcoming to attendees who may find it hard to follow along only by listening.
Solutions
Video conferencing has also created a space that can solve problems that existed during in person meetings as well. Taking it a step further than auto captions and transcription, Zoom also offers automated live translation in multiple languages. Eliminating the barrier of language opens opportunities for increased cooperation on business and personal levels across the globe.
At the core of all this progress and these big initiatives are the small pieces of data coming together to make it all possible. Those auto captions that make it easier to understand speakers with unfamiliar accents don’t happen without the data sets that were used to train the AI creating them.
The quality of these data sets determines the quality of the captions, translations, and transcriptions we receive. When the smallest error, such as a “does” becoming a “doesn’t,” can change the meaning of an entire sentence, the accuracy of the AI doing the work is of the utmost importance.
When it comes to video conferencing, any AI doing transcription, captioning, or translating needs to be well trained in conversational and spontaneous speech. Video conference meetings often experience overlapping speech from multiple participants as many people maybe talk at once and unexpected outbursts when another person is talking.
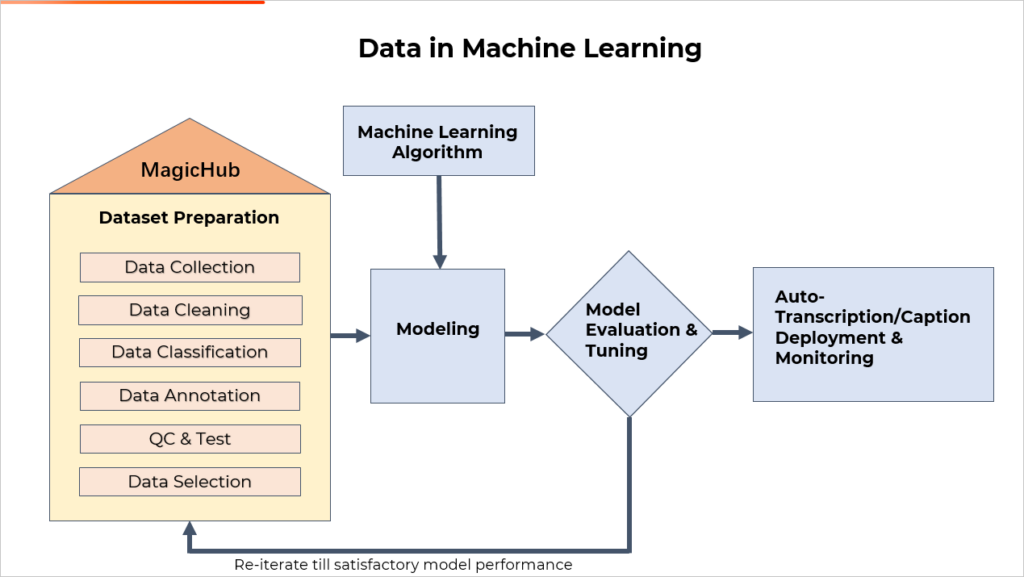
The process of acquiring and then cleaning and categorizing high quality data is incredibly time consuming and if not done well, can lead to major issues with AI performance. As the limits of video conferencing platforms continue to be pushed, Magichub seeks to provide a solution to the never-ending search for high quality data sets. Currently, Magichub can provide AI developers with data sets for spontaneous speech and conversational speech corpuses for multiple languages including English, Mandarin Chinese, American English, Korean, Japanese, German, Spanish and etc. For AI developers seeking to push their video conferencing to the next level in terms of efficiency and accessibility, these data sets provide machine learning them with the data they need to seamlessly incorporate natural and accurate AI into their model.
Recommendations
In this case, we recommend below datasets to you:
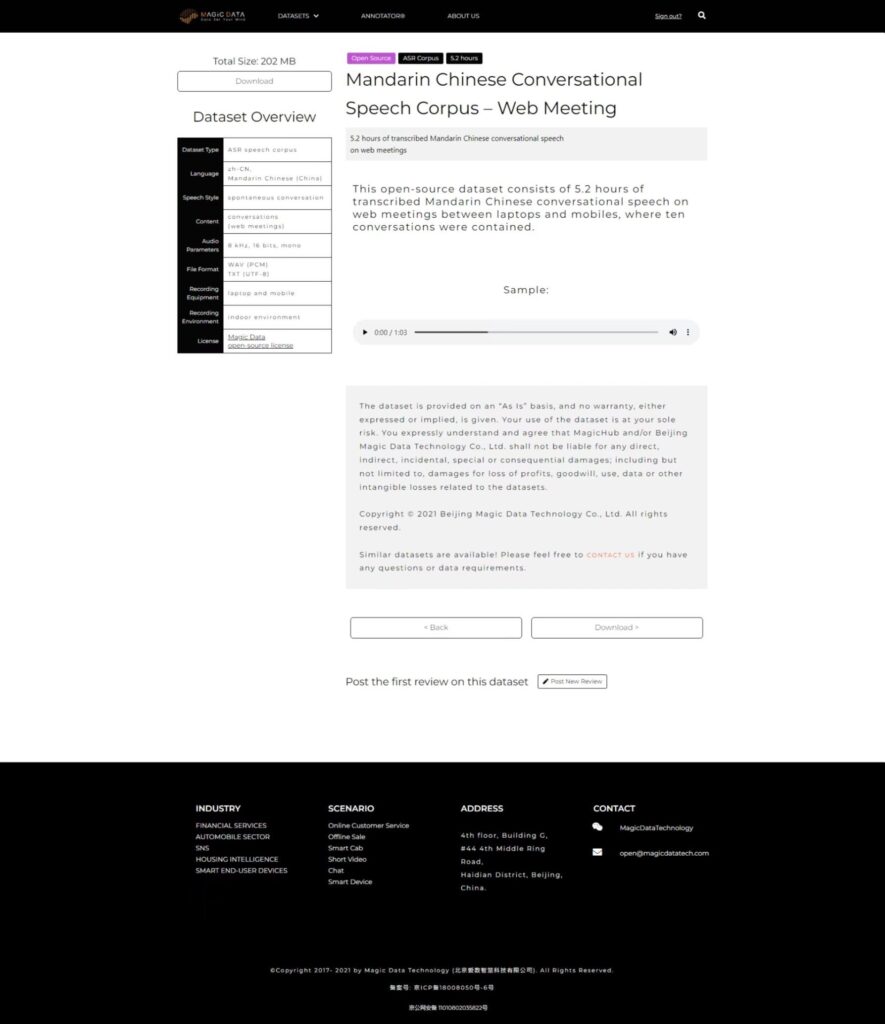
Mandarin Chinese Conversational Speech Corpus – Web Meeting https://magichub.com/datasets/mandarin-chinese-conversational-speech-corpus-web-meeting/
While the challenge of getting that one coworker to finally remember to unmute when they speak may never be solved, we have the data to meet the AI related challenges facing the future of video conferencing development. With our focus on natural and conversational speech, our data provides machine learning engineers with a solid foundation for their AI developments.
To learn more about the datasets mentioned in this article go to magichub.com.
About Magichub Community
Magichub community is an data-centric AI community that provides resources for AI developers to promote innovation and progress within the field. Aside from the actual open-source data, Magic Hub also provides a space for data producers and users to ask questions, give advice, and collectively problem solve. This open-source community also gives us insight into the specific trends in challenges that AI developers may be facing and allows us to create data sets as solutions to those challenges. As AI has created new levels of accessibility within video conferencing, Magichub seeks to do the same in the world of machine learning and data annotation. Our goal is not just to produce high caliber data sets to meet the needs of the current level of AI, but to be part of the progress into the future of machine learning. While we have many excellent data sets for open source, here at Magichub we understand the importance of open-source data to the future of AI and machine learning.