In recent years, AI has become well ingrained into the field of customer service. Many companies use it to streamline customer interactions and provide a more efficient experience for the consumer and the employee. One of the major areas of growth within the field of customer service when to AI, is the rise of the chatbot assistant. It is commonplace now to click on a website and have box pop up offering assistance or answers to questions. Anyone who has called in to a company’s customer service line has probably also dealt with some form of AI that either answers their questions or uses its own questions to determine the best place to send the call.
Not only has AI been introduced to this field for the benefit of the customer, but it is quite a cost-saving tool for companies as well. As chatbot assistants become more advanced, they are able to take on more of the roles that had previously been filled by human employees. Anyone who has worked in a customer service position knows the pain of answering the same question over and over, day after day. Many of these questions are simple and have straightforward answers but take up much of the day of a customer service agent. This is one area that AI chatbot assistants have thrived. Many of these questions can now be answered without a customer having to speak to a live agent at all. Of course, some issues can only be addressed by live agents, but having customers go through a chatbot assistant first, can eliminate many of the repetitive questions and help streamline the process of getting customers to the correct department.
The benefits for companies of more AI in customer service tend to snowball from each other. As less live agents mean less use of office space and utilities and can bring down overhead costs for a company significantly. While this is a double-edged sword and can also impact job security for employees, when AI is implemented in tandem with live agents, it can make their jobs easier by cutting down on monotonous, repetitive work.
While the benefits of AI chatbot assistants are numerous for companies and do often make for a more efficient customer experience, their efficacy is highly dependent on the quality if the AI. Much focus is put on developing algorithms and actual programming of the AI, but these factors will still fall short if the foundation is weak. That foundation, and the foundation of all AI, is data. While high quality data cannot guarantee high quality AI, low quality data can almost certainly guarantee poor quality AI. Most people have already had experience with the AI, specifically chatbots, that were developed using poor quality data. It is an experience that usually ends with the customer yelling some variation of “LIVE PERSON” into their phone repeatedly as the AI continues to incorrectly diagnose their needs. A chatbot assistant that merely riles a customer up to be sent to a live agent, is not much of an assistant. Anything built on a poor foundation is likely to crumble, which is why the AI world, especially in the US, is seeing a shift toward a more data-centric approach to AI development and machine learning. Instead of the major focus being on algorithmic development, that focus has been widening to acknowledge and appreciate the importance of the data at the core of the AI.
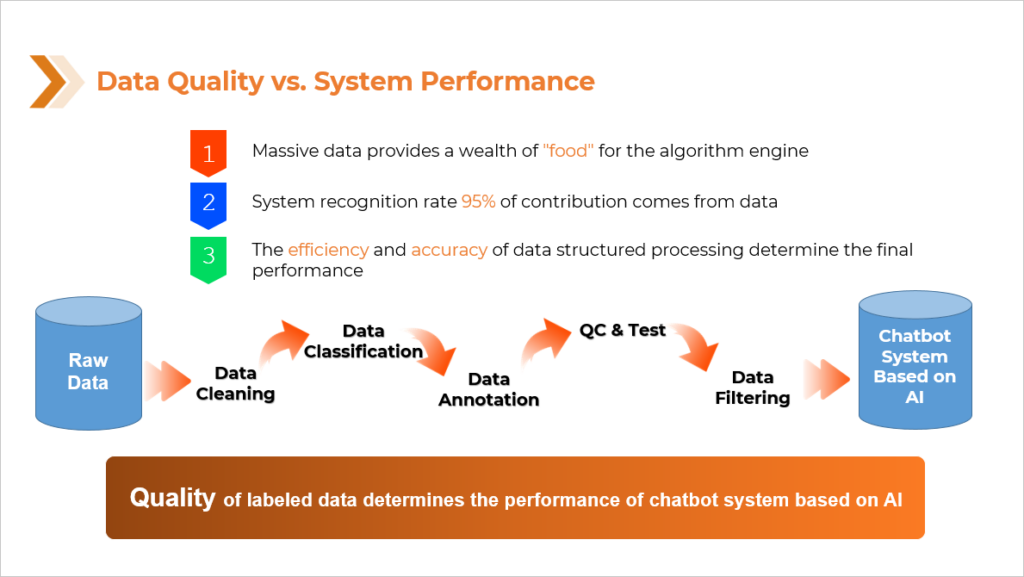
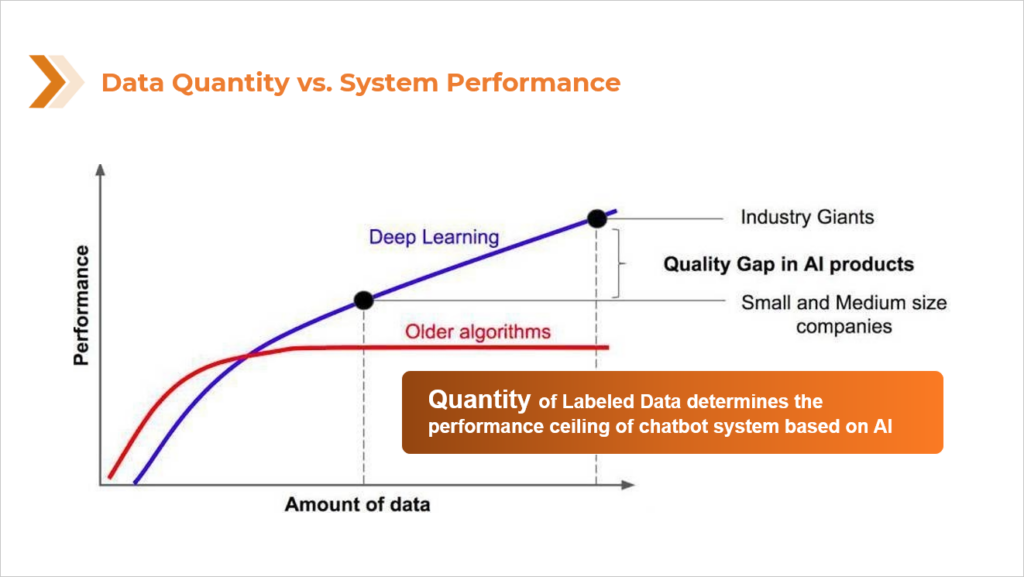
There is by no means a shortage of data to be used in the process of training AI but one of the reasons poor quality data is so prevalent, is, quite simply, that data annotation is hard. It is a tedious process that demands strict attention to detail and a piece-by-piece approach to make sure the quality of each piece of data meets the criteria needed. But not every company or AI developer is going to have time and/or resources to collect and annotate their own data. They may not have access to the population needed to collect the data from or the systems in place to go through each piece of data and ensure its quality.
MagicHub seeks to provide a solution for companies and machine learning engineers seeking to take a more data-centric approach in the creation of their AI. MagicHub is a community that provides access to high quality open-source data sets for AI engineers. This platform provides a huge relief in the process of AI development as it solves the problem that has been a thorn in the side of many AI developers.
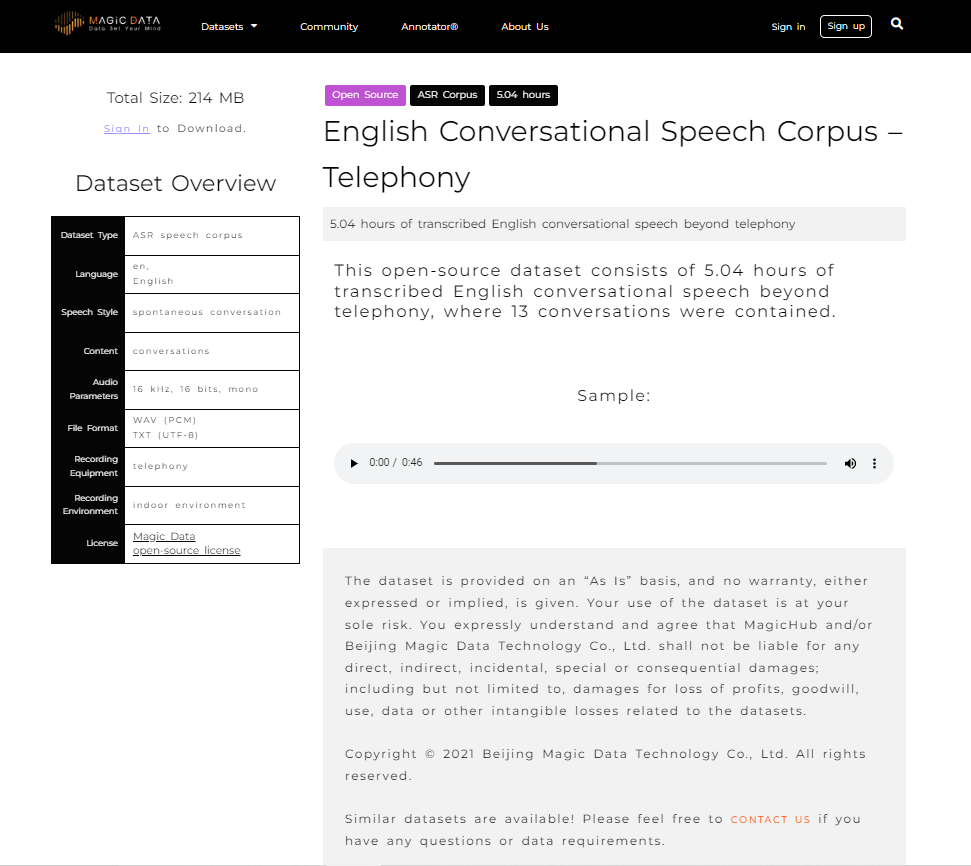
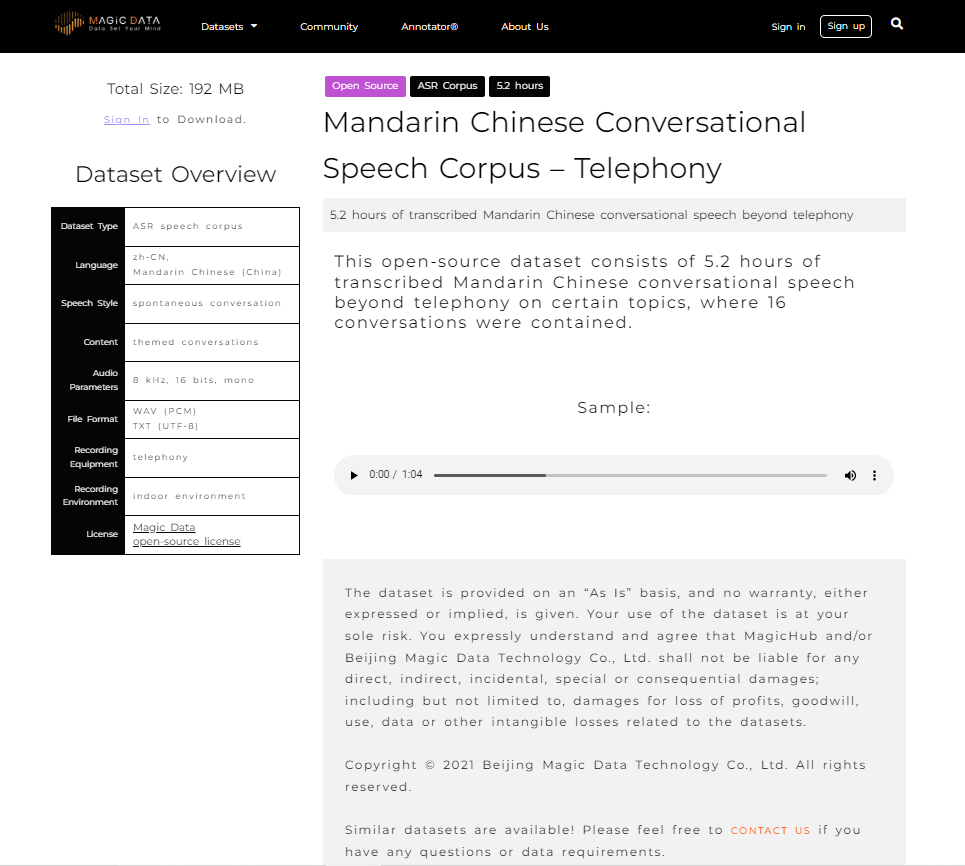
With many AI programs, and specifically chatbot assistants, there is a need for conversational data. A chatbot will receive inquiries and calls from a wide variety of people and need to be able to understand multiple accents, dialects, and even different languages. Aside from the way people speak, the words they use often stray from the standardized version of their language and contain variations of slang words and various pronunciations. MagicHub provides access to a large number of data sets that focus of conversational language and spontaneous speech to meet this need. These are not limited to English and MagicHub also provides conversational data in English, Chinese, Spanish, Japanese, Korean and German, to name a few. Because MagicHub is cooperative open-source ecosystem, the amount of high-quality data will only grow from here.
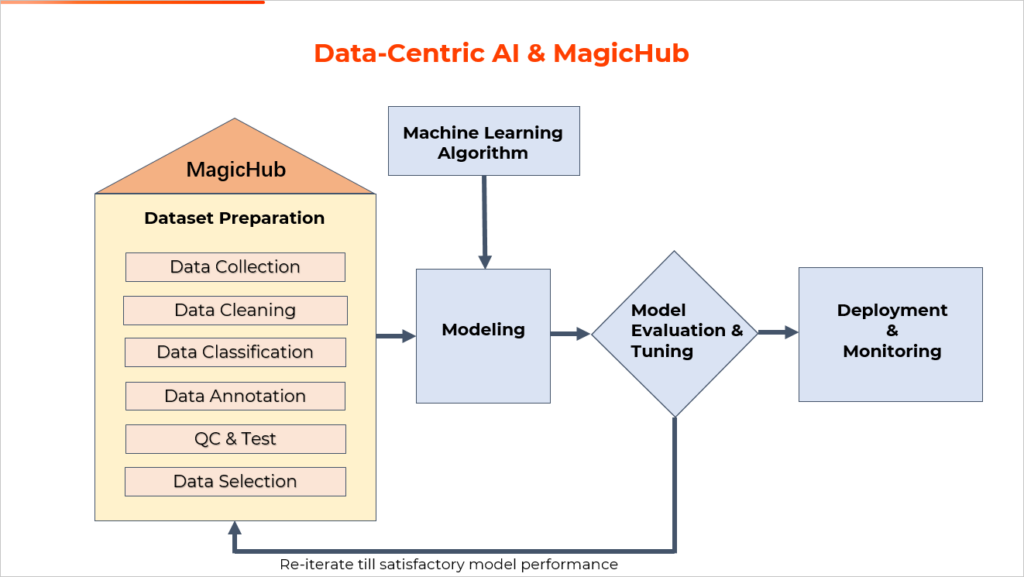
As AI advances in the field of customer service and the roles it plays become more complex and require more interaction with customers, the more obvious bad foundations will be. Because of this, the shift to a more data-centric approach to AI development is looking more and more necessary. MagicHub seeks to be at the center of this and at the forefront of pushing AI development by providing that strong and steady foundational data to more AI developers and machine learning engineers.